Botarell / Spain
Botarell / Spain
Botarell – Mechanical-Biological Waste Treatment Plant Featuring Kompogas® Technology
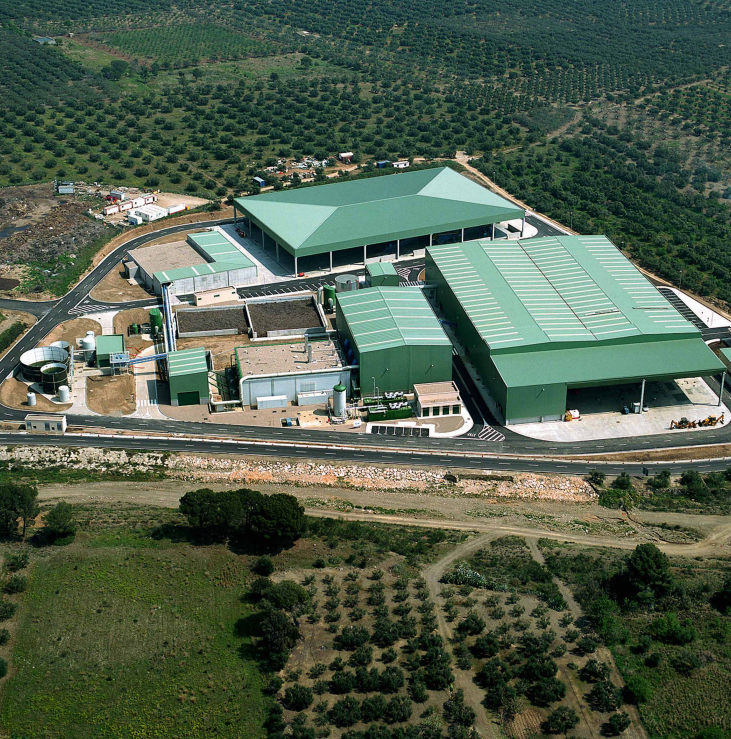

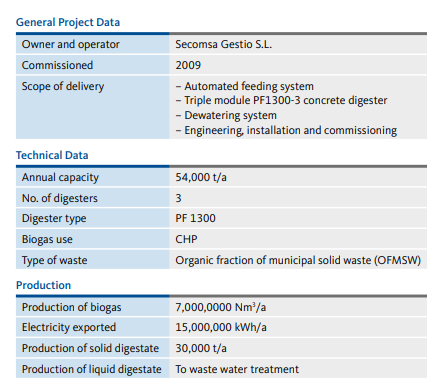
At the core of the mechanical-biological waste treatment plant in Botarell, are three horizontal plug-flow Kompogas® digesters by Kanadevia Inova. They are used to ferment the organic fraction separated out from municipal solid waste and convert it into biogas and fertilizer. This process closes the materials cycle by generating renewable energy from organic waste.
Supplying the Region with Energy
The plant in Botarell was commissioned by the Catalan regional authority Baix Camp under a public private partnership (PPP), and is operated by a semipublic operating company in collaboration with Acciona Services. The mechanical-biological treatment facility (MBT) processes municipal waste from almost 100 communities in the Reus/Tarragona region. Since 2009 the plant has enabled the production of electricity for around 2,500 households from biowaste, and the recycling of both organic and non-organic materials. Prior to that, the region’s municipal waste had been dumped or incinerated.
Kompogas® Technology
The facility runs on a fully automated basis, fed non-stop, 365 days a year, using a fully automated crane system to enable constant generation of high-grade biogas. The robust construction of the plant’s Kompogas® triple module PF1300-3 digesters guarantees problem-free operation even with a high proportion of impurities (glass, plastic, metal, etc.) in the organic input material. The compact layout of the digesters also means they take up little space, which in turn has had a positive impact on the total investment involved in the project.
From Pre-Treatment to Energy Utilization
In the mechanical processing line the organic fraction is separated out from the municipal waste and taken by conveyor to an intermediate storage bunker. A fully automated crane system then feeds substrate into the Kompogas® digesters, where it spends around 14 days decomposing under anaerobic conditions at a temperature of 55 °C. The biogas generated is cleaned and fed into two cogeneration units that produce electricity and heat. The heat is used to maintain the temperature in the digesters, while the green power is fed into the public grid. The digestate is pumped out by a discharge pump at the other end of the digesters and fed into the dewatering system, where screen screw presses separate it into liquid and solid digestate. The solid digestate is refined further in a composting plant with closed tunnels and open windrows, and then recycled as biological covering material for golf courses or roads. Part of the liquid digestate is used to inoculate the fresh substrate,while the excess process water is purified in the plant’s water treatment unit and put back into the environment.