Herefordshire & Worcestershire / UK
Herefordshire & Worcestershire / UK
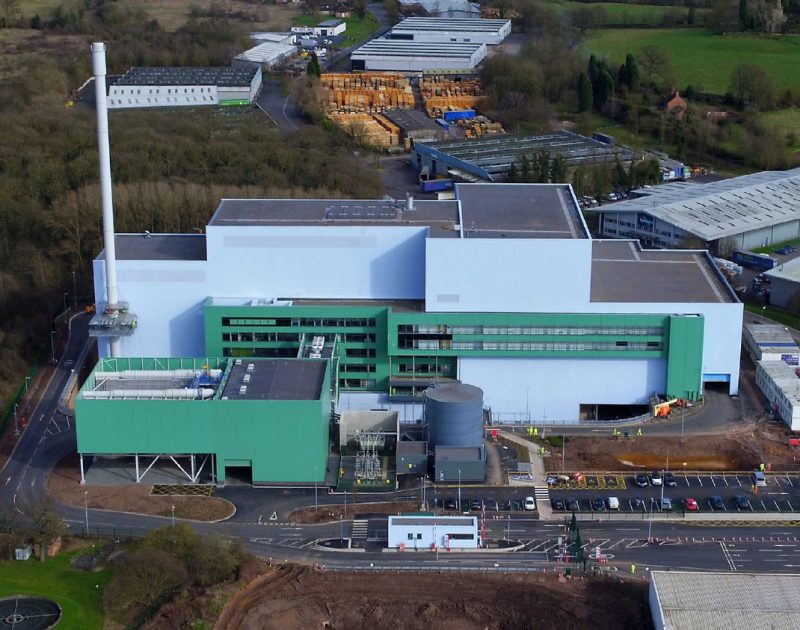
Fulfilling Recycling and Diversion Targets: Envirecover Energy Recovery Facility.
Waste avoidance, reuse, recycling, minimisation – and then? Thermal treatment of residual waste with environmentally safe production of renewable energy is just another piece in today’s waste management puzzle. Kanadevia Inova and its technology is a reliable partner for Mercia Waste Management and the two counties of Herefordshire and Worcestershire in achieving these objectives.
Multiple Parties with One Goal
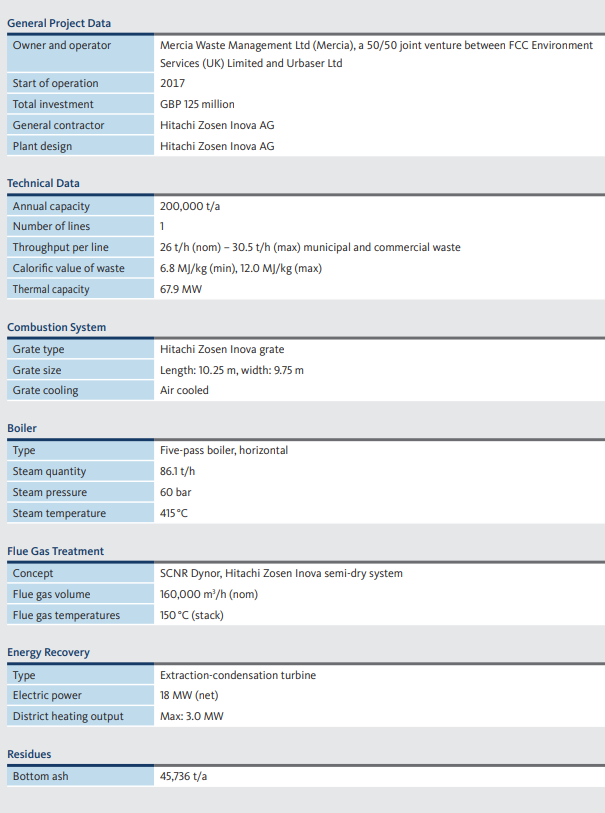
As the first PFI project in the UK, a Waste Management Contract was signed between the Councils of Herefordshire and Worcestershire and Mercia Waste Management Ltd (Mercia) in December 1998. Mercia is a 50/50 joint venture between FCC Environment Services (UK) Limited and Urbaser Ltd. Kanadevia Inova, which has been delivering reliable thermal waste treatment technology since 1933, already has WtE references with both parties. In concluding the contract in 2014, all partners joined forces to enable the two counties to realise their waste strategy: avoidance, reuse, recycling, minimisation, and recovery of energy.
Compact Design to Meet Planning Requirements
As planning was sensitive to height, an innovative design was chosen that included construction into the ground, leading to a roofline only 35 m above ground level. This required careful planning of all construction activities as these take part at different levels at the same time. Nevertheless, Kanadevia Inova managed to deliver a competitive project program while strictly adhering to its rule of safety first.
Energy for the Region
The Energy Recovery Facility at Hartlebury helps the two councils to become more independent from centralised power stations and to increase their renewable portion, as defined for instance in Worcestershire’s 2015 Draft Renewable Energy Research Paper. With its designed steam conditions of 60 bar and 415 °C, the single line plant achieves a net efficiency of approximately 25%. An R1 factor above 0.65 will make it one of the leading energy recovery facilities in the country.
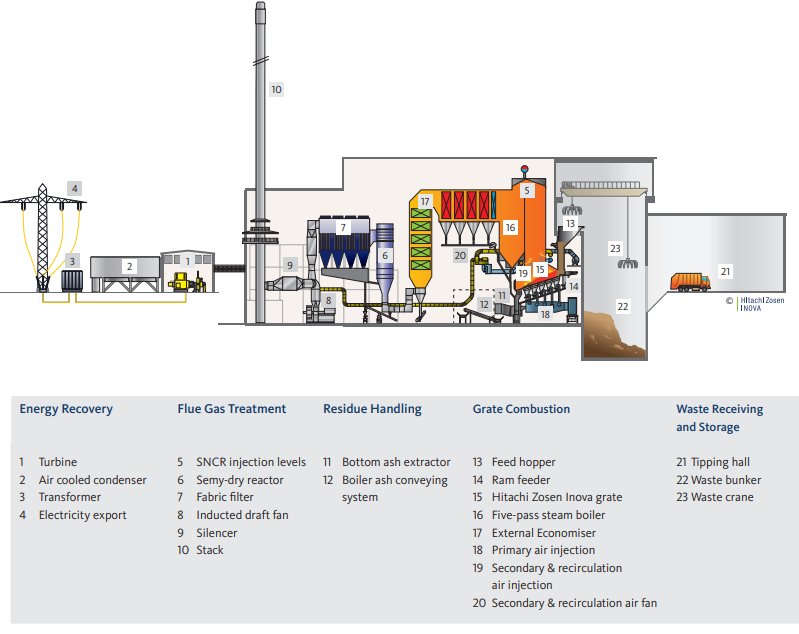
Reliable and Proven Energy Recovery
The incoming waste is stored in a bunker allowing for approx. 5 days of storage. The fully automatic crane provides thoroughly mixed waste and feeding into the hopper. The feed hopper with its staged/staggered system provides the necessary air seal to ensure a controlled combustion process. The flexible control of the ram feeder as well as the five individually controllable grate zones guarantee an optimal waste layer and residence time on the Kanadevia Inova grate, and thus a comprehensive burn-out, independent of the waste composition or calorific value. Primary air taken from the bunker is introduced from underneath the grate and secondary air plus recirculated flue gas is
tangentially injected at high velocity into the secondary combustion chamber above the grate.
This ensures intensive mixing and results in the thorough burn-out of combustion gases. The energy released during combustion and burn-out is transferred to the water/steam circulation loop in the 68 MW horizontal five-pass boiler.
Clean Process for Clean Energy
The plant is equipped with Kanadevia Inova’s proven SNCR system and subse-quently a lime and activated carbon-based semi-dry system. Water injection cools down the flue gas to approx. 145°C while at the same time also reactivating unused lime in the recirculated material. After safe removal of fine particulates, contaminants, dioxins, and any remaining heavy metals, an induced draft fan blows the clean flue gas into the 83-meter high stack. Its design and fully automated air pollution control system safeguards strict compliance with EU emission limits. This is checked before leaving the stack by a continuous measurement system that has an online connection to the environmental agency. Moreover, the setup is also designed to be able to cope with potential future changes in emission limits.
Residues and By-Products
The captured contaminants will be stabilized and the residues processed for disposal at appropriately permitted facilities. The inert bottom ash can be processed further for use as a road aggregate.